Introduction: Heart diseases represent a growing and alarming public health concern in Bangladesh. In recent years, the prevalence of heart diseases has been on the rise, with these conditions becoming the leading cause of death in the country, responsible for a substantial 21.1% of total deaths in 2020. This comprehensive overview aims to shed light on the prevalent heart diseases in Bangladesh, focusing on their types, risk factors, prevention strategies, and available treatments. By understanding the landscape of heart diseases in Bangladesh, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to mitigate this pressing health issue.
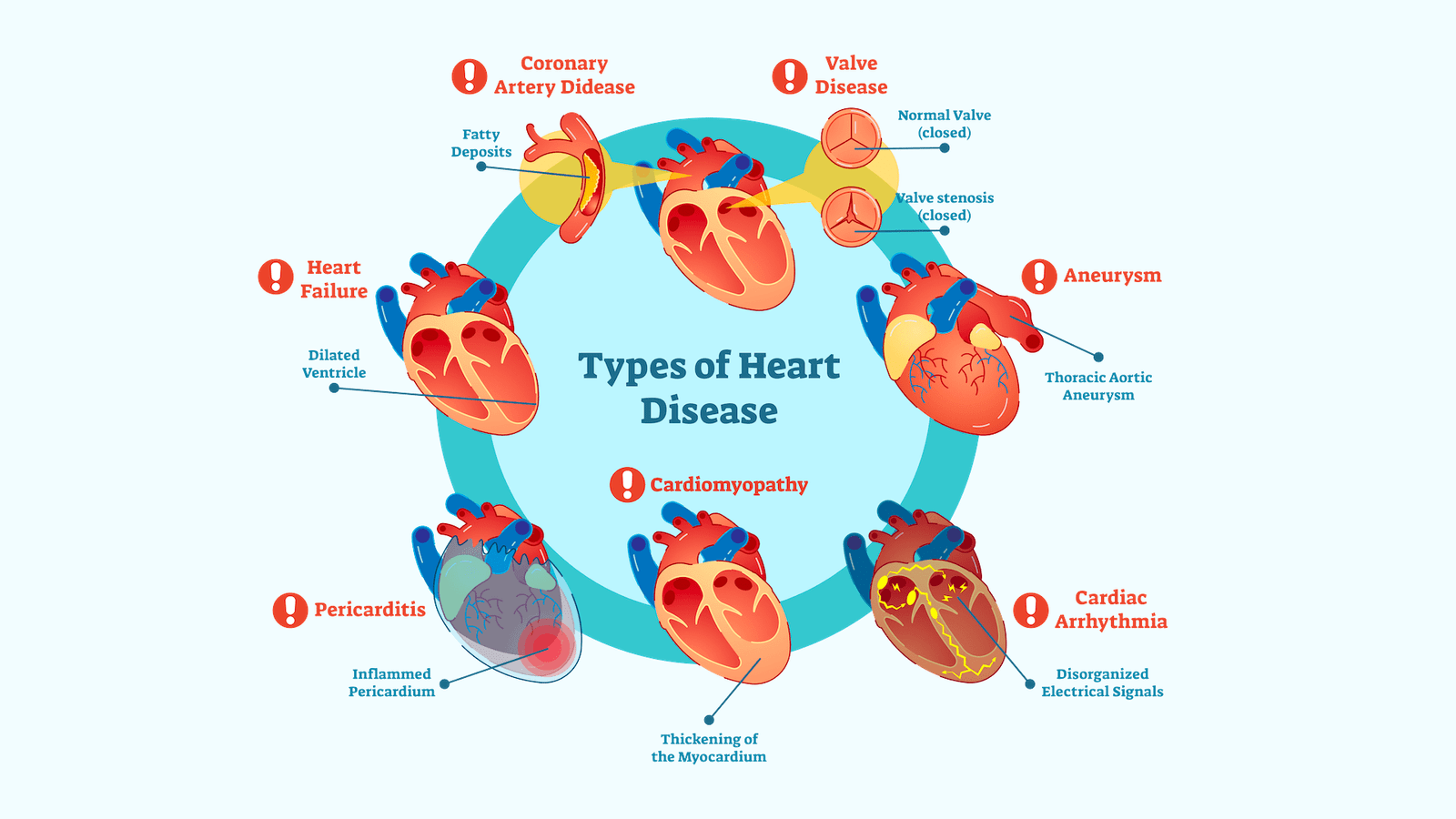
Prevalence and Types of Heart Diseases
The common types of heart diseases in Bangladesh include:
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
- CHD is the most prevalent heart disease in Bangladesh, constituting a significant 65% of all heart diseases.
- It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque in the arteries supplying blood to the heart. This plaque buildup can lead to a heart attack, resulting from the blockage of blood supply to the heart.
Stroke
- Strokes occur when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, often due to blood clots or ruptured blood vessels.
- Strokes can lead to various disabilities, including paralysis, speech difficulties, and memory loss.
Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD)
- RHD is a heart disease caused by rheumatic fever, which is a complication of untreated strep throat.
- It can lead to damage to the heart valves, ultimately culminating in heart failure.
Hypertension
- Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for heart disease, capable of damaging arteries and making them more prone to plaque buildup.
Heart Failure
- Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot efficiently pump blood, often attributed to factors like CHD, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Other Heart Diseases:
Additional heart diseases common in Bangladesh encompass conditions like:
- Cardiomyopathy: A disease affecting the heart muscle, causing thickening, enlargement, or stiffening.
- Arrhythmia: A condition in which the heart beats irregularly, either too fast or too slow.
- Congenital Heart Disease: A birth defect affecting the heart’s structure.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Several factors contribute to the high prevalence of heart disease in Bangladesh:
Unhealthy Diet
- Diets high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sugar elevate the risk of heart disease.
Physical Inactivity
- Sedentary lifestyles contribute significantly to the risk of heart disease.
Smoking
- Smoking damages arteries and increases the risk of blood clots.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure and damage the heart muscle.
Diabetes
- Diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease.
High Blood Pressure
- High blood pressure damages arteries and increases the likelihood of plaque buildup.
High Cholesterol
- Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to plaque accumulation in the arteries.
Family History
- Individuals with a family history of heart disease are at an increased risk of developing the condition themselves.
Prevention of Heart Disease
- The best approach to prevent heart disease in Bangladesh is to adopt a healthy lifestyle. This includes:
Healthy Diet
- Prioritize diets that are low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sugar, while emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Regular Exercise
- Engage in routine physical activity to promote heart health.
Weight Management
- Maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise.
Smoking Cessation
- Quit smoking to mitigate the risk of heart disease.
Alcohol Moderation
- Limit alcohol consumption to healthy levels.
Managing Chronic Conditions
- People with diabetes and high blood pressure should carefully manage their conditions to reduce the risk of heart disease.
Treatment for Heart Disease
The treatment for heart disease varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and exercise.
- Medications to manage risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Surgical interventions, such as angioplasty and coronary artery bypass surgery.
- In some cases, a combination of these approaches is necessary.
Conclusion
Heart diseases are a critical public health issue in Bangladesh, with a growing prevalence and an alarming impact on mortality rates. However, the situation is not without hope. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and accessing timely medical care, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing heart disease.
Additional data reveals that the prevalence of heart disease is higher in urban areas than in rural areas of Bangladesh, more common in men than women, and increasingly affecting younger people. The mortality rate from heart disease in Bangladesh is higher than in most other developing countries, highlighting the urgent need for continued awareness, prevention, and treatment efforts.